Android Architecture: Communication between ViewModel and View
Introduction
There’s been a lot of talk about MVVM architecture since Google announced architecture components last year at I/O and so many developers who preferred Presenters (including me) have started to accept the ViewModel world. Using ViewModels (over Presenters) reduces boilerplate code, manages data during configuration change, makes it easy to share data between multiple fragments. However, it does make communication with Views much harder.
To learn complete android course visit:android online training
Problem
Let’s take an example of Edit Profile screen. User data must be validated before sending to server, which means Presenter/ViewModel should be able to show/hide progress indicator, send validation and server errors (if any) to the View. Also if city/gender dialog is visible during configuration change then View should be notified about that as well.
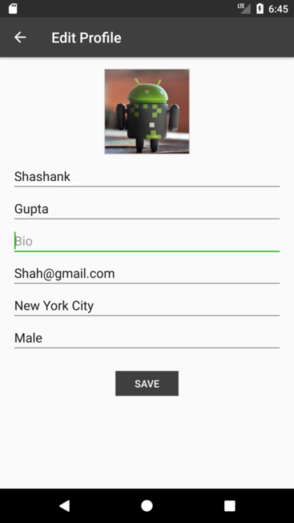
Presenters and ViewModels shouldn’t hold references to Views.
In case of Presenter we usually define some sort of Contract interface where View implements Contract.view and Presenter implements Contract.presenter. And now Presenter can easily call methods on View.
interface EditProfileContract
{
interface view
{
fun setProgress(show: Boolean)
fun showEmptyFirstNameError()
fun showEmptyLastNameError()
}
interface presenter
{
fun saveProfile(firstName: String, lastName: String, bio: String, email: String, city: City, gender: String)
}
}
ViewModel on the other hand is more loosely coupled with the View. We usually expose data using LiveData or RxJava. Once View is subscribed to the ViewModel, it starts to receive updates. This approach works pretty well when passing data to Views but problem arises when ViewModel needs to communicate View state, progress indicator status, validation/server errors.
Solution
Fewer the LiveData/Observable, better it is. So what we are looking for is a way to aggregate the information that needs to be passed to the View. In most cases ViewModel needs to communicate three things:
- Data → This is something that needs to be presented on the View like user object for user profile or feed items for social feed. Most code samples show how to pass data from ViewModel to View so I’ll leave it out for brevity sake.
- Status → This could be anything which needs to be passed only once like validation errors, no network error, server errors.
enum class Status
{
SUCCESS,
ERROR,
NO_NETWORK,
EMPTY_FIRST_NAME,
EMPTY_LAST_NAME,
EMPTY_CITY,
INVALID_URI
}
Live data doesn’t provide any out of the box solution but there’s an implementation of it called SingleLiveEvent provided in Google samples which works pretty well in here. Create a SingleLiveEvent which expose status LiveData to View layer.
status LiveData to View layer.
private val status = SingleLiveEvent<Status>()
fun getStatus():
LiveData<Status>
{
return status
}
fun handleImage(intent: Intent?)
{
intent?.data?.let
{
avatar.value = it.toString()
}
?: run { status.value = Status.INVALID_URI
}}
View just observe status LiveData and performs action based on different status/errors. In this example we can easily show different toast/snackbar for each error.
viewModel.getStatus().observe(this, Observer { handleStatus(it) })
private fun handleStatus(status: Status?)
{
when (status)
{
Status.EMPTY_FIRST_NAME -> Toast.makeText(activity, "Please enter your first name!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
Status.EMPTY_LAST_NAME -> Toast.makeText(activity, "Please enter your last name", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
Status.EMPTY_CITY -> Toast.makeText(activity, "Please choose your home city", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
Status.INVALID_URI -> Toast.makeText(activity, "Unable to load the photo", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
Status.SUCCESS ->
{
startActivity(HomeFragment.newIntent(activity))
activity.finish()
}
else -> Toast.makeText(activity, "Something went wrong, please try again!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
- State → UI state like progress indicator, dialogs, which should be passed to the View every time it starts observing ViewModel data. Simply we can create a data class to hold the state.
data class EditProfileState(
var isProgressIndicatorShown: Boolean = false,
var isCityDialogShown: Boolean = false,
var isGenderDialogShown: Boolean = false)
Create state as MutableLiveData in ViewModel. And since we only expose LiveData to View layer, we should also provide setters for View to update it’s state.
private val state = MutableLiveData<EditProfileState>()
fun getState(): LiveData<EditProfileState> { return state}
fun setProgressIndicator(isProgressIndicatorShown: Boolean) { state.value?.isProgressIndicatorShown = isProgressIndicatorShown}
fun setCityDialogState(isCityDialogShown: Boolean) { state.value?.isCityDialogShown = isCityDialogShown}
fun setGenderDialogState(isGenderDialogShown: Boolean) { state.value?.isGenderDialogShown = isGenderDialogShown}
Show or hide City/Gender dialog in View layer based on the state data.
viewModel.getState().observe(this, Observer { handleState(it) })
private fun handleState(state: EditProfileState?) { if (state?.isCityDialogShown == true) { showCitySelectionDialog() return } if (state?.isGenderDialogShown == true) { showGenderSelectionDialog() return }}
Summary
Aggregating information(loading status, UI state, errors) would help keep the ViewModels lean and clean. For me status and state approach worked out pretty well.
If you have any suggestions I’d love to hear them. Happy coding!
To more android course tutorials visit:android app development course
Comments
Post a Comment